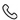Research and hair clone
What kind of future innovations and development plans is AHT preparing
Hair Multiplication
Hair Multiplication
Hair multiplication is a procedure in which extracted hair or fragments are implanted directly into the scalp (in vivo). All in hope that hair it self will regenerate.
The concept behind hair multiplication, by using the extracted hairs, tells us that it is a simple, non-invasive method. This methods use prepared tray that can be used to introduce and align newly born cells in a new location.
There is a hope that, during hair transplantation, in the stage of removal of a small part of the cells by extraction, sufficient tissue will be provided for the formation of new follicles, while the number of old ones will not decrease.
The disadvantage of this method lies in the fact that extracting hair usually leads to something else. It leads to the appearance of a hair that does not have enough cells to stimulate the generation of new follicles.
Hair Cloning
Hair cloning or genetic engineering of new hairs is a promising procedure, but it is still in the experimental phase. Scientists are able to isolate the germline or "stem cells" of the hair follicle, or even other cell types.
They isolate the fibroblast at the root and differentiate them to the full growth of new follicles in the laboratory. Under ideal conditions, this could lead to an infinite accumulation of donor hairs that would help in hair transplantation. It would be used to fill the thinning area while at the same time the donor area remains untouched.
There are several promising reports from scientists from all over the world, primarily based on laboratory experiments on animals. Unfortunately there is no real evidence or scientific data that these treatments could be available to patients in the next few years.
Cloning of the hairs remains a great hope for the future.

Hair cloning
Isolating genes
Scientists from all over the world are making efforts to isolate a larger number of genes responsible for various types of androgenic alopecia. All effort is made in order to make this method of hair transplantation faster and more efficient. For now, we know that a certain number of genes play a role in the onset of androgenic alopecia. Genes such as age, pattern and evolution are one of them. A complete understanding of the genetic androgenic alopecia can lead in the future to genetic testing.
That would establish the diagnosis of androgenic alopecia during childhood. Some of thus would be possible to carry out appropriate genetic treatment. The efforts are aimed at isolating the genes responsible for the androgenic alopecia common in this population. Also there is attempts to confirm a possible relationship between androgenic alopecia, diet and environmental factors (e.g. smoking).
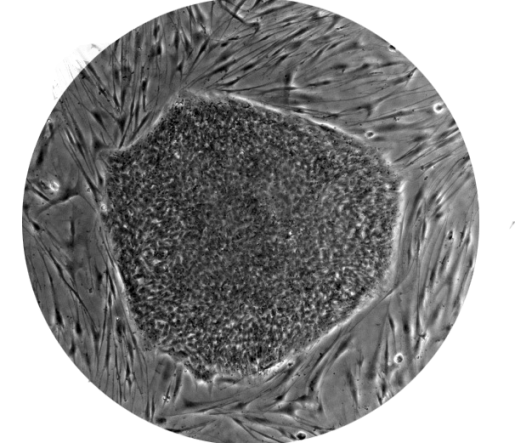
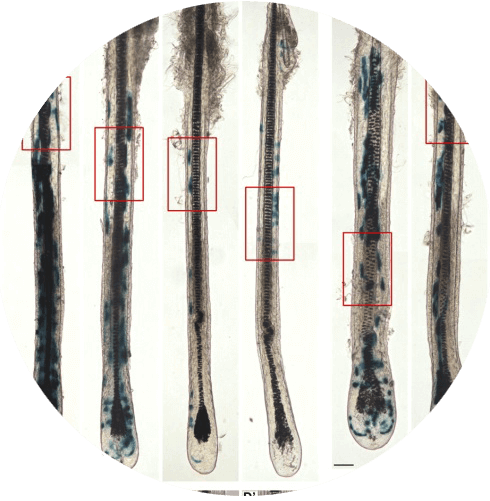
Stem cells
Stem Cells
In connection with hair cloning, research is taking place around the world in the stem cells field.
There are various reports claiming that, hypothetically, stem cells could be differentiated into different types of human cells, since they are primarily undifferentiated cells.
There are a lot of stem cells in the fatty tissue. Some speculations exist that the injection of fatty tissue, isolated from the abdomen into the balding area, will lead to the stimulation of unused hair follicles in the area.
That could cause new hair growth. According to recent reports, hair follicles that are in a state of rest in the balding area still contain a small number of stem cells. If this steam cells are stimulated, they could give new hairs.
Although stem cell research is interesting and promising, it is still at the level of experimentation and undetermined. Alternative type of baldness treatment is not yet precisely defined as such.
ACell’s Extracellular Matrix
ACell's Extracellular Matrix (ECM) is a natural biological material that can be implanted at the place of an injury or damaged tissue, in order to accelerate healing. The ECM is a complex mixture of proteins and glycosaminoglycans. Glycosaminoglycans (GAGs) are linear polysaccharides composed of two basic saccharides: an amino sugar and an uronic acid.
Graft stimulates the cells of the body to form new tissues specific to that place (this process is called "autocloning"). Therefore, instead of the organism producing scar tissue, the healing happens by restoration with new tissue. Studies conducted in the ECM area have shown that the tissues are remodeled very quickly by promoting neovascularization (the growth of new blood vessels) and employing mesenchymal cells that have been left without a “host“ (collagen releasing cells which have the ability to promote hair formation).
These effects result in faster wound healing, while scars, in hair transplantation, are less noticeable. The possibility of using biologically based matrices in the process of hair multiplication is real. For sure it takes a lot of work to make hair multiplication become a treatment with practical application in the treatment of baldness.
Our clinic is currently studying the use of the ECM option for multiplying hairs at the back of the head, as well as facilitating wound healing in hair transplantation interventions.